Numbness in the hands is a common problem amongst those aged between 40 to 60 years. It can be mildly annoying or disabling, and sometimes is accompanied by severe pain. It usually means a nerve is constricted, and should never be ignored, as permanent nerve damage with loss of sensation and strength may result if left untreated.
“The most common conditions causing numbness in the hands are carpal tunnel syndrome and cubital tunnel syndrome.“
What is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Carpal tunnel syndrome causes numbness, tingling or burning pain in the thumb, index, middle or ring fingers. The median nerve, which is the main nerve providing sensation to the hand, goes through a narrow space in the wrist, called the carpal tunnel. In some people, especially women, this space is narrower, and any increase in the pressure within this space will decrease blood flow to the median nerve, causing it to malfunction. Gripping an object tightly, using a mobile phone or even holding up a newspaper can also trigger these symptoms. Shaking the hands vigorously usually relieves the symptoms.
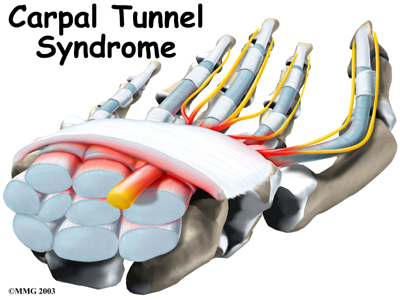
Over time, the ability to feel becomes worse and the thumb muscles may become weak and waste away, resulting in difficulty performing simple tasks like doing up buttons or picking up coins. Out of every 1,000 people, three to five will develop carpal tunnel syndrome. People who do a lot of repetitive work with their hands such as production line workers and homemakers, and those who work long hours at the computer keyboard with poor posture are at greater risk. Pregnant women are also susceptible due to water retention. It is also common among diabetics, those with renal failure, hypothydroidism and rheumatoid arthritis.
What are the Treatments for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Early or mild carpal tunnel syndrome can be treated by keeping the wrist in a brace especially when sleeping, and avoiding postures and activities that increase the pressure around the nerve. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication, high dose Vitamin B6 and anti-inflammatory injections around the nerve may also provide temporary relief. The best long-term solution is to permanently decompress the nerve.
This involves a surgical procedure to cut the hands of tissue constricting the nerve. It is commonly done with a 3cm incision in the palm. This takes about two weeks to heal. As the wound is rather small, the hand can be used for most daily activities the very next day after surgery.
What is Cubital Tunnel Syndrome?
Cubital tunnel syndrome is less common, but causes more disability. This condition affects younger adults, especially those who do repetitive work with the elbows bent most of the time. It may also affect older people with arthritis in the elbow.
What are the Symptoms of Cubital Tunnel Syndrome?
The symptoms of this are numbness in the small and ring fingers, along with clumsiness and difficulty straightening these fingers. Symptoms are usually worse in the morning and when doing activities requiring prolonged elbow flexion such as working with a keyboard or playing some musical instruments. Over time, sensation in these fingers can be lost completely, and the small muscles of the hand can become completely paralysed, weakening the whole hand and making it difficult to manipulate small objects such as keys.
What are the Cause of Cubital Tunnel Syndrome?
This is caused by constriction of the ulnar nerve, which is the main nerve to the small muscles of the hand and supplies sensation to the little finger. It goes through the cubital tunnel, a narrow space behind the elbow and under the forearm muscles on its way to the hand. This is the “funny bone” that causes tingling in the fingers when the inner part of the elbow is knocked against a hard surface. Some people have a narrower space or thick bands of tissue going across the nerve, making them more prone to constriction.
What are the treatments for Cubital Tunnel Syndrome?
The treatment is similar to carpal tunnel syndrome. The elbow needs to be rested and kept in extension as much as possible. When sleeping, a brace should be used to keep the elbow from bending. Physiotherapy is done to try and free the nerve. Surgery is recommended if symptoms do not resolve after three months of conservative treatment. After the surgery, the pain is less, and the arm can be used for most daily activities the very next day.
Numbness in the Hands Specialist
Dr Mathew Tung, Nerve Specialist

