Brief Outline of Ankle Supination
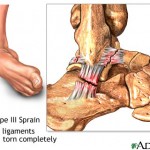
Supination is the outward rolling of the foot at the ankle. This is a normal movement during the push-off phase of running, walking, or jumping. Excessive supination can cause damage to the ligaments, tendons, and muscles of the lower leg. Acute over-supination may cause stretching or tearing of the ligaments of the foot and ankle. Excessive supination can lead to a weakening of the ankle structure and decreased stability.
Anatomy and physiology
Supination involves the bones of the ankle joint, but more specifically, the subtalar joint. The distal (lower) ends of the tibia and fibula rest on the talus of the foot and allow for movement of the foot. This is traditionally referred to as a hinge joint because its main function is to allow flexion and extension of the foot. It does, however, allow limited pronation and supination as well, which is normal during running, walking, and jumping. These movements aid balance and improve shock absorption.
Cause of Ankle Supination
Weak or loose tendons and ligaments in the ankle. Weak or fatigued muscles of the lower leg. Forceful outward rolling of the ankle. Improper or worn footwear. Uneven or sloped running (or landing) surface.
Signs & Symptoms of Ankle Supination
Pain in the arch, heel, and/or knees and hips. Instability in the ankle. Pain over the outside of the ankle. Pain may be immediate with acute over-supination (such as an ankle sprain).
Complications if Left Ankle Supination Unattended
May lead to chronic weakness and instability to the ankle. The pain and improper gait may lead to compensation and injury to other structures and tissues. The ligaments may loose their elasticity from excessive stretching, and tearing may occur.
Treatment for Ankle Supination
Rest, ice, and anti-inflammatory medications to help alleviate the pain. Acute over-supination may require medical attention and immobilisation. Chronic supination will require correction of the underlying problems, whilst allowing adequate rest for the tissues to recover.
Rehabilitation & Prevention for Ankle Supination
Proper warm-up is essential. Strengthening and stretching of the muscles of the lower leg may help support the ankle, keep it moving in the correct plane, and reduce excessive supination. Orthotics and gait analysis may be required. Gradual return to a full workload is recommended and retraining of the athlete to improve, or correct running form is important. Ensure proper footwear and a smooth flat running (or landing) surface.
Long-term Prognosis for Ankle Supination
Will respond well if treated early with a good rehabilitation plan. The length of time the condition is allowed to persist will also affect the recovery time. In rare cases, surgery may be required to tighten the tendons or correct skeletal factors.